By: CS2103-AY1819S1-T13-1 Since: Aug 2018 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Features
- 3.1. Viewing help :
help - 3.2. Adding a person:
add - 3.3. Editing a person :
edit - 3.4. Listing all persons :
list - 3.5. Adding tuition time of a student :
addTime - 3.6. Edit certain class time of certain student:
exchangeTime - 3.7. Deleting tuition time of a student :
deleteTime - 3.8. Deleting grade of a student :
deleteGrade - 3.9. Locating persons by name:
find - 3.10. Locating persons by address:
find/a - 3.11. Locating persons by email address:
find/e - 3.12. Locating persons by phone number:
find/p - 3.13. Deleting a person :
delete - 3.14. Selecting a person :
select - 3.15. Filter students by tuition fee:
filterByFee - 3.16. Filter students by educational level:
filterByEducation - 3.17. Filter students by grade:
filterByGrade - 3.18. Filter students by time slot:
filterByTime - 3.19. Give Suggestions to students:
suggestion - 3.20. Give Suggestions to students:
suggestionByIndex - 3.21. Listing entered commands :
history - 3.22. Grades attribute
- 3.23. Promote students stored in TutorPal :
promote - 3.24. Analyzing grades commands
[coming in v2.0] - 3.25. Retrieving earnings
- 3.26. Undoing previous command :
undo - 3.27. Redoing the previously undone command :
redo - 3.28. Clearing all entries :
clear - 3.29. Exiting the program :
exit - 3.30. Saving the data
- 3.31. Encrypting data files
[coming in v2.0]
- 3.1. Viewing help :
- 4. FAQ
- 5. Command Summary
1. Introduction
TutorPal is for private tutors who prefer to use a desktop app for managing students information. More importantly, TutorPal is optimized for those who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). TutorPal is a great tool to track students' academic performance and schedule. Jump to the Section 2, “Quick Start” to get started. Enjoy!
2. Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java version
9or later installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
Tutor Pal.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your Tutor Pal.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
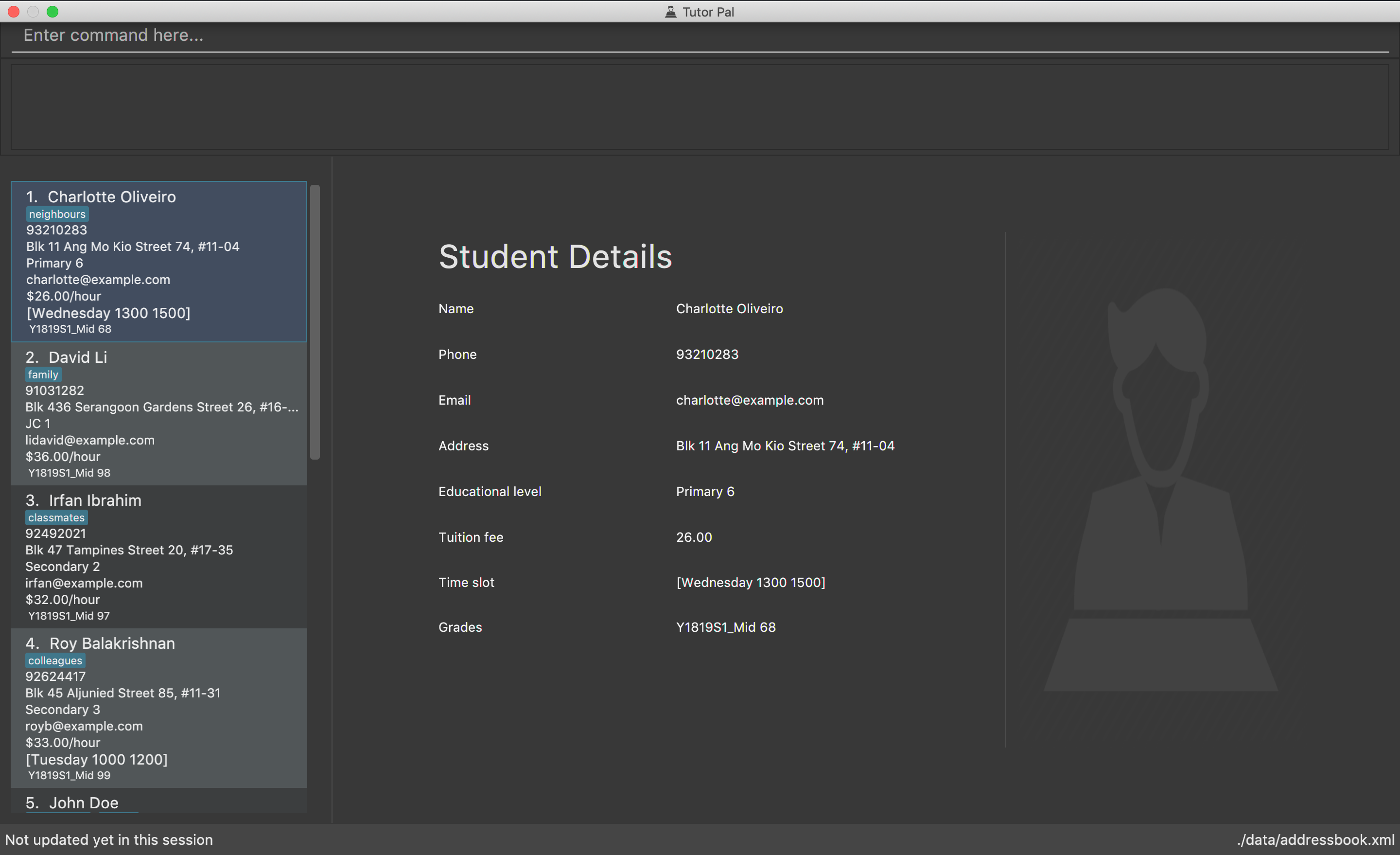
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
list: lists all contacts -
addadd n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 el/Primary 4 g/Y1819S1_Mid 89 t/friends t/owesMoney: adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the Address Book. -
delete3: deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to Section 3, “Features” for details of each command.
3. Features
Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items,Grades in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items,Grades with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,g/midterm 100,t/friend t/family,g/test1 100 g/test2 99etc. -
Grade consists of two parts, exam name and exam score.
-
The name and score should be separated by space.
-
Score should be between 0 and 100.
-
Considering the grades are just some records, the APP didn’t implement the delete function temporarily. If you input a wrong exam name, use undo to fix it.
-
-
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable.
3.1. Viewing help : help
Format: help
3.2. Adding a person: add
Adds a person to the student list
Format: add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS el/EDUCATIONAL_LEVEL [g/GRADE]… [t/TAG]…
|
Examples:
-
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 el/Primary 4
Add a person without grade and tag. -
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 el/Primary 4 g/Y1819S1_Final 100 g/Y1819S1_Mid 89 t/friends t/owesMoney
Add a person with one or more than one grades and tags.
3.3. Editing a person : edit
Edits an existing person in the student list.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [el/EDUCATIONAL_LEVEL] [g/GRADE] [t/TAG]…
Examples:
-
edit 1 p/91234567 e/alex@example.com
Edits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andalex@example.comrespectively. -
edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/
Edits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags. -
edit 5 el/Secondary 1
Edits the educational level of the 5th student to Secondary 1. -
`edit 2 g/Y1819S1_Mid 100 `
Change the score of an exam. -
edit 1 g/test1 100 g/test2 99
Add more new grade records for a student.
|
By editing the educational level of any student using this command will remove any "Graduated" |
3.4. Listing all persons : list
Shows a list of all persons in Tutor Pal.
Format: list
3.5. Adding tuition time of a student : addTime
Adds a tuition timing for a student in Tutor Pal.
Format: addTime INDEX ts/TIME
Example:
-
addTime 1 ts/mon 1300 1500
Adds the tuition timing that is on Monday which starts on 1300hour and ends on 1500hour for the 1st person shown in the displayed person list in Tutor Pal.
3.6. Edit certain class time of certain student: exchangeTime
Exchange class time between two students who are in the same grade of same education level
Format: exchangeTime A_TIME_SLOT_ORDINAL_NUMBER B_TIME_SLOT_ORDINAL_NUMBER n/NAME_A n/NAME_B
Examples:
-
exchangeTime 0 0 Alice BobExchange Alice first time slot and Bob first time slot.
|
The reason this command exists is that when two student want to swap time it cannot only use edit because the existing time-slot will crush. If the two students are not in the same grade of same education level It will be considered as invalid command. The ordinal number of the time is 0 base. If the the corresponding time-slot doesn’t exit based on the ordinal number, then return invalid input. |
3.7. Deleting tuition time of a student : deleteTime
Deletes a tuition timing for a student in Tutor Pal.
Format: deleteTime INDEX ts/TIME
Example:
-
deleteTime 1 ts/mon 1300 1500
Deletes the tuition timing that is on Monday which starts on 1300hour and ends on 1500hour for the 1st person shown in the displayed person list in Tutor Pal.
3.8. Deleting grade of a student : deleteGrade
Deletes a grade record for a student in the address book.
Format: deleteGrade INDEX NAME_OF_EXAM
-
NAME_OF_EXAMmust already exist in the student’s grade records. -
The student with the index
INDEXwill have the grade namedNAME_OF_EXAMdeleted.
Example:
-
deleteGrade 1 Y1819S1_Mid
Deletes grade record named "Y1819S1_Mid" for the first person in the display panel.
3.9. Locating persons by name: find
Finds persons whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]…
Examples:
-
find John
ReturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
find challotto
ReturnsCharlotte Oliveiro -
find David Roy John
Returns any person having namesDavid,Roy, orJohn
3.10. Locating persons by address: find/a
Finds persons whose addresses contain all the given keywords.
Format: find/a KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]…
Examples:
-
find/a B311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25
ReturnsJohn Doe -
find/a B311, CLEMENTI Ave 2, #02-25
ReturnsJohn Doe(case insensitive) -
find/a #02-25, Ave 2 Clementi, B311
ReturnsJohn Doe(the order of the keywords does not matter) -
find/a serangoon
Returns person whose addresses containing the keywordSerangoon, i.e.Bernice YuandDavid Li -
find/a srangon
Returns persons whose addresses containing the keywordSerangoon, i.e.Bernice YuandDavid Li(fuzzy matching)
3.11. Locating persons by email address: find/e
Finds a person through his/her email address.
Format: find/e EMAIL [MORE_EMAILS]…
Examples:
-
find/e John@example.com
ReturnsJohn Doewhose email address isJohn@example.com -
find/e LIDavd@example.com
ReturnsDavid Liwhose email address islidavid@example.com(case insensitive) -
find/e lidavd@exmple.com
ReturnsDavid Liwhose email address islidavid@example.com(fuzzy matching)
3.12. Locating persons by phone number: find/p
Finds a person through his/her phone number.
Format: find/p PHONE_NUMBER [MORE_PHONE_NUMBER]…
Examples:
-
find/p 98765432
ReturnsJohn Doewhose phone number is98765432 -
find/p 9876543
ReturnsJohn Doewhose phone number is98765432(fuzzy matching) -
find/p 98765433
ReturnsJohn Doewhose phone number is98765432(fuzzy matching)
3.13. Deleting a person : delete
Deletes the specified person from the student list.
Format: delete INDEX
Examples:
-
list
delete 2
Deletes the 2nd person in the student list. -
find Betsy
delete 1
Deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.
3.14. Selecting a person : select
Selects the person identified by the index number used in the displayed person list.
Format: select INDEX
Examples:
-
list
select 2
Selects the 2nd person in the student list. -
find Betsy
select 1
Selects the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.
3.15. Filter students by tuition fee: filterByFee
List all the students whose tuition fee is greater or equal to the input fee.
Format: filterByFee FEE
Examples:
-
filterByFee 24returns a list of students whose tuition fee is greater or equals to $24/hour.
|
If no students qualify the filter criteria, an empty list is returned along with a system message which says that no such students can be found. |
3.16. Filter students by educational level: filterByEducation
List all the students with given educational level
Format: filterByEducation EDUCATIONAL_LEVEL
Examples:
-
filterByEducation Secondary
returns a list of students whose Education level is Secondary.(no matter which year he or she is in) -
filterByEducation JC
returns a list of students whose Education level is JC.(no matter which year he or she is in)
|
If no students qualify the filter criteria, an empty list is returned along with a system message which says that no such students can be found. The input of the education level must be "JC" "Secondary" or "Primary". Other input will be considered invalid input. |
3.17. Filter students by grade: filterByGrade
List all the students whose grades fall between the minimum and maximum grade(both inclusive).
Format: filterByGrade MINIMUM_GRADE MAXIMUM_GRADE
Examples:
-
filterByGrade 50 100
returns a list of students whose has grade within 50 and 100 (both 50 and 100 are inclusive).
|
If the input minimal grade is larger than maximal grade, then it will be regarded as the range between maximal and minimal grade. If no students qualify the filter criteria, an empty list is returned along with a system message which says that no such students can be found. |

3.18. Filter students by time slot: filterByTime
List the student who has class at the given time.
Format: filterByTime ts/TIME_SLOT
Examples:
-
filterByTime ts/mon 1300 1400
returns the student whose has tuition time in monday 1300-1400.
|
The time must be followed as format like "mon 1300 1400" and only "mon" "tue" "wed" "thu" "fri" "sun" "sat" are considered valid date. If no students qualify the filter criteria, an empty list is returned along with a system message which says that no such students can be found. |
3.19. Give Suggestions to students: suggestion
Give Suggestions to students
Format: suggestion NAME
Examples:
-
suggestion AliceShow the suggestion to Alice according to her performance.
|
If the student has not taken any exam before No suggestion gonna be shown. |
3.20. Give Suggestions to students: suggestionByIndex
Give Suggestions to students
Format: suggestion index (base 1)
Examples:
-
suggestion 1Show the suggestion to the first student in the list according to his or her performance.
|
If the student has not taken any exam before No suggestion gonna be shown. |
3.21. Listing entered commands : history
Lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
Format: history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
3.22. Grades attribute
Grade attribute consists of two parts, exam name and exam score.
|
Add grade:
You can add some grades record for a student, both using add command and edit command.
Example
add g/mid-test 100 [other part]
edit 1 g/mid-test 100
|
Edit grade will not delete the previous grades as tap attribute. |
Change grade:
if you need to change the score of a exam, you can use edit as well.
3.23. Promote students stored in TutorPal : promote
Promotes educational grade of the selected student(s)
Format: promote [INDEX]…
-
Promotes the educational grade of the students specified by their index.
-
There can be more than one INDEX provided.
|
Multiple indexes should be separated by a space. |
Format: promote all
-
Promotes all students stored in TutorPal, including those who are not displayed on the panel.
Examples
-
promote 1 2 4 12
Promotes the first, second, fourth and twelfth student. -
promote all
Promotes all students in TutorPal.
3.24. Analyzing grades commands [coming in v2.0]
Analyze the grades of students
Format: grades ACTION [parameters]
|
Regard the mark of the student who doesn’t have a grade as 0. |
3.25. Retrieving earnings
Retrieve the total earnings from tuition fees from all students between a range of date in the current year.
Format: earnings START_DATE END_DATE
-
START_DATEandEND_DATEshould be given in the format of DDMM. -
The beginning and ending dates are included in the calculation of tuition fees.
-
The year field is not required as TutorPal assumes current calender year by default.
-
To calculate the amount of money earned within a day, input the same
START_DATEandEND_DATE. -
Graduated students and students without tuition time slot(s) are ignored by the earnings function.
-
Due to the lack of built-in attendance taking capability in TutorPal, the earnings function:
-
Follows a standard one lesson per week schedule and does not account for cancelled or ad-hoc lessons.
-
Should only be used to calculate tuition fees that will be earned in the future.
-
Does not account for the tuition fees of graduated students.
-
|
While the use of earnings command for dates before the current date is not prohibited, it is not encouraged as the values calculated will be inaccurate if tutorPal contains either graduated students and/or students whom had their time slot(s) changed before. |
Example:
-
earnings 0204 2506
This command returns the total amount of tuition fees earned between 2 April 2018 to 25 June 2018 inclusive. A warning message will be displayed to remind the user on the useage of past dates. -
earnings 1212 1212
This command will return the total amount of tuition fees to be earned on 12 December.
3.26. Undoing previous command : undo
Restores the address book to the state before the previous undoable command was executed.
Format: undo
|
Undoable commands: those commands that modify the address book’s content ( |
Examples:
-
delete 1
list
undo(reverses thedelete 1command) -
select 1
list
undo
Theundocommand fails as there are no undoable commands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
3.27. Redoing the previously undone command : redo
Reverses the most recent undo command.
Format: redo
Examples:
-
delete 1
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command) -
delete 1
redo
Theredocommand fails as there are noundocommands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies theclearcommand)
3.28. Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the address book.
Format: clear
3.29. Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
3.30. Saving the data
Address book data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
3.31. Encrypting data files [coming in v2.0]
{explain how the user can enable/disable data encryption}
4. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous Tutor Pal folder.
5. Command Summary
-
Add :
add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS el/EDUCATIONAL_LEVEL [g/GRADE]… [t/TAG]…
e.g.add n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 el/JC 1 g/FinalExam 85 -
Add time :
addTime INDEX ts/TIME
e.g.addTime 1 ts/mon 1300 1500 -
Clear :
clear -
Delete :
delete INDEX
e.g.delete 3 -
Delete time :
deleteTime INDEX ts/TIME
e.g.deleteTime 1 ts/mon 1300 1500 -
Earnings :
earnings START_DATE END_DATE -
Promote :
promote all -
Promote :
promote INDEX…
e.g.promote 1 2 5 13 -
Edit :
edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [el/EDUCATIONAL_LEVEL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
e.g.edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com el/JC 1 -
Edit time :
editTime n/NAME ts/OLD_TIME_SLOT ts/NEW_TIME_SLOT
e.g.editTime n/Alice ts/mon 1300 1400 ts/tue 1300 1400 -
Exchange time :
exchangeTime NAME_A A_TIME_SLOT_ORDINAL_NUMBER NAME_B B_TIME_SLOT_ORDINAL_NUMBER
e.g.ExchangeTime Alice 0 Bob 0 -
Filter by fee :
filterByFee FEE
e.g.filterByFee 24 -
Filter by educational level :
filterByEducation EDUCATIONAL_LEVEL
e.g.filterByEducation Secondary -
Filter by grade :
filterByGrade MINIMUM_GRADE MAXIMUM_GRADE
e.g.filterByGrade 50 100 -
Filter by time :
filterByFee TIME_SLOT
e.g.filterByTime mon 1300 1400 -
Find :
find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
e.g.find James Jake -
Find by address :
find/a ADDRESS
e.gfind/a serangoon -
Find by phone number :
find/p PHONE
e.gfind/p 12345678 -
Find by email :
find/e EMAIL
e.gfind/e lidavid@example.com -
Help :
help -
History :
history -
List :
list -
Redo :
redo -
Select :
select INDEX
e.g.select 2 -
Suggestion :
suggestion NAME
e.g.suggestion Alice -
Undo :
undo